

The Harvard Style stipulates that you must cite in two places:
In the body of the text of your essay/document, this is called an In-text citation or In-text reference
In the Reference List or Bibliography at the end of the essay/document
There are two main types of In-text citation:
Paraphrasing: A restatement of a text or passage in your own words (This is most commonly used)
Direct quotation: Reproduction of a phrase or passage from a book, articles, report. etc.
In-text citation: Paraphrasing examples (Idea taken from another and put in one's own words)
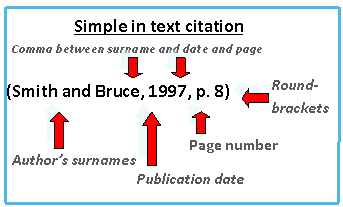
Use the surname(s) of the author(s) and the date of publication, also include the page number if it is a specific idea
On the subject of employee motivation, Evenden and Anderson (1992, p. 45) suggest that in order to improve motivation for appraisal, that an objective for each key area of a job need to be developed
Further examples of different ways to include the in-text reference in a sentence
In-text citation: Further Examples
Pagination: whether to use a page number
In-Text Citation (Author date, page number) - use this in the body of your paper after a direct quote or when paraphrasing a passage, summarising an idea from a particular page or you want to direct the reader to a specific page.
Use the Surname(s) of the author(s) and the date of the publication, (and the page number if a book)
As a general rule (which varies depending on subject matter), quotations should be less than 10% of your total word count
When quoting a page or paragraph from a book the page number is always required within the in-text citation
Examples of In-text citation for quotes:
If the quotation is of 30 words or over then it should be: (a) On a separate paragraph, (b) In a one size smaller font, (c) Left indented, (d) No quotation marks, (e) Preceded by a full colon.
In speaking of the relationship between empowerment and self-efficacy, French (2005) has this to say:
The concept of empowerment is founded on the belief that everyone has an internal need for self-determination and a need to cope with environmental demands directly. This suggests that appropriate empowerment strategies can raise the perception of low self-efficacy. Self-efficacy refers to a person's belief that they can perform adequately in a situation. (p.185)
2 Authors:
(Smith and Doheny, 2003, p. 31)
Multiple authors :
You can use the first author surname 'et al.' for in-text citations for multiple authors
However in your full reference you must list all authors - see examples on Tab C of this guide.
According to Critser et al., 'all human psychology is influenced by upbringing'. (2003, p. 31)
or
'All human psychology is influenced by upbringing'. (Critser et al., 2003, p. 31)
If you refer to a source which you have not read, but which is mentioned in a source you have read, you cite both in your in-text reference but include only the work you have actually read in the full reference list at the end.
In text examples
text....(Allen, 2001 cited in Parker, 2009, p.45)
A study by Allen (2001, cited in Parker, 2009, p. 45) showed that…
or
according to Allen, 2001 (cited in Parker, 2009, p. 45) there is ample evidence to claim ...
Full Reference example:
In your full list of references you should include only the work you have read, i.e. the primary reference; in this instance 'Parker'.
Parker, N.L. (2009) Strategic management. Mason, Ohio: Thomson South-Western
These are distinguished by lower-case letters following the year
Example:
Note: The sources should be cited chronologically by year of publication with the most recent source first. If more than one work is published in the same year, then they should be listed alphabetically by author/editor.
Use the author of the chapter and and date of the book in your in text reference
Full reference see Reference format Books
Example in-text citation for Appendices:
Your Own Appendix
Add your appendix immediately following your reference pages and label it as Appendix A, B, C, etc. Use these labels when discussing the appendix in the body of your paper. In the paper, after the sentence in which you are referencing your appendix, format the in-text citation as (See Appendix A). The letter should match the appropriate appendix label. Do not cite your own appendix on the reference page. If there is only one Appendix just refer to it as Appendix
Another Author's Appendix
When using an appendix from another author, include this information on your reference page. For example, a citation on the reference page for an appendix found in a book should read: Author. (year). Appendix A of Title of work. Location: Publisher. The appendix letter should match the appropriate section you are using.
An in text reference to an appendix can also give some more details:
Example: Inner city mental health care access continues to be a problem (see Appendix for a table showing mental health care access by city).
Overview: all in-text referencing information
The Harvard Style stipulates that you must cite in two places:
In the Reference List or Bibliography at the end of the essay/document
In the body of the text of your essay/document, this is called In-text citation

There are two main types of In-text citation:
Direct quotation: Reproduction of a phrase or passage from a book, articles, report. etc.
Paraphrasing: A restatement of a text or passage in your own words
In-text citation: Paraphrasing examples
In-text paraphrasing (Idea taken from text but put in different words)
Use the Surname(s) of the author(s) and the date of the publication, also include the page number for books if it is a specific idea
On the subject of employee motivation, Evenden and Anderson (1992, p. 45) suggest that in order to improve motivation for appraisal, that an objective for each key area of a job need to be developed
Further examples of different ways to include the in text reference in a sentance
In-text citation: Further Examples
Pagination: whether to use a page number
In-Text Citation (Author date, page number) - use this in the body of your paper after a direct quote or when paraphrasing a passage, summarising an idea from a particular page or you want to direct the reader to a specific page. When referencing journal articles do not include a page number
In-text citation: Direct Quotation examples:
Use the Surname(s) of the author(s) and the date of the publication, (and the page number if a book)
As a general rule (which varies depending on subject matter), quotations should be less than 10% of your total word count
When quoting a page or paragraph from a book the page number is always required within the in-text citation
Example of an extended quote
If the quotation is of 30 words or over then it should be: (a) On a separate paragraph, (b) In a one size smaller font, (c) Left indented, (d) No quotation marks, (e) Preceded by a full colon.
In speaking of the relationship between empowerment and self-efficacy, French (2005) has this to say:
The concept of empowerment is founded on the belief that everyone has an internal need for self-determination and a need to cope with environmental demands directly. This suggests that appropriate empowerment strategies can raise the perception of low self-efficacy. Self-efficacy refers to a person's belief that they can perform adequately in a situation. (p.185)
In-text referencing for Multiple Authors (3 or more)
2 Authors:
(Smith and Doheny, 2003, p. 31)
Multiple authors :
You can use the first author surname 'et al.' for in-text citations for multiple authors
However in your full reference you must list all authors - see examples on Tab C of this guide.
According to Critser et al., 'all human psychology is influenced by upbringing'. (2003, p. 31)
or
'All human psychology is influenced by upbringing'. (Critser et al., 2003, p. 31)
In-text citation for a secondary reference
If you refer to a source which you have not read, but which is mentioned in a source you have read, you cite both in your in-text reference but include only the work you have actually read in the full reference list at the end.
In text examples
text....(Allen, 2001 cited in Parker, 2009, p.45)
A study by Allen (2001, cited in Parker, 2009, p. 45) showed that…
or
according to Allen, 2001 (cited in Parker, 2009, p. 45) there is ample evidence to claim ...
Full Reference example:
In your full list of references you should include only the work you have read, i.e. the primary reference; in this instance 'Parker'.
Parker, N.L. (2009) Strategic management. Mason, Ohio: Thomson South-Western
Two or more documents with the same author and year of publication
These are distinguished by lower-case letters following the year
Example:
Referring to two different sources at the same time
Note: The sources should be cited chronologically by year of publication with the most recent source first. If more than one work is published in the same year, then they should be listed alphabetically by author/editor.
Use the author of the chapter and and date of the book in your in text reference
Full reference see Reference format Books
Appendices In-Text Referencing
Example in-text citation for Appendices:
Your Own Appendix
Add your appendix immediately following your reference pages and label it as Appendix A, B, C, etc. Use these labels when discussing the appendix in the body of your paper. In the paper, after the sentence in which you are referencing your appendix, format the in-text citation as (See Appendix A). The letter should match the appropriate appendix label. Do not cite your own appendix on the reference page. If there is only one Appendix just refer to it as Appendix
Another Author's Appendix
When using an appendix from another author, include this information on your reference page. For example, a citation on the reference page for an appendix found in a book should read: Author. (year). Appendix A of Title of work. Location: Publisher. The appendix letter should match the appropriate section you are using.
An in text reference to an appendix can also give some more details:
Example: Inner city mental health care access continues to be a problem (see Appendix for a table showing mental health care access by city).
Figures and tables in the appendices are labeled A1, A2, B1, and so forth, according to the appendix in which they appear. (Note: Omit the letter if there is only one appendix.)